How does virtual desktop work? You really don’t know? don’t worry I’m here with you to explain What is virtual desktop and how does virtual desktop work? keep reading…
In today’s digital world, remote work and work-from-home policies have become increasingly popular. As a result, businesses are turning towards virtual desktop solutions to help them manage their IT resources more efficiently.
Virtual desktops have become a crucial component of the modern workplace, as they offer users a way to access their work environment remotely.
In this article, we will explore the basics of virtual desktops and how they work.
So first of all we know the real definition of virtual desktop.
Definition of Virtual Desktop (VDI)
A virtual desktop is a form of desktop computing that is hosted on a remote server or cloud platform. Unlike a traditional desktop, a virtual desktop is accessed via the internet using remote desktop software.
Virtual desktops allow users to access their work environment from anywhere, on any device. This provides a more flexible and efficient way of working, as it removes the need for a physical workstation.
Importance of Virtual Desktop:
Virtual desktops offer several benefits for businesses of all sizes. One of the primary benefits is increased mobility. With virtual desktops, employees can work from anywhere, on any device.
This provides a more flexible and efficient way of working, as it removes the need for a physical workstation. Additionally, virtual desktops are more secure than traditional desktops, as all data is stored on a central server.
This means that if a device is lost or stolen, there is no risk of data loss or theft.
Virtual desktops are also more cost-effective than traditional desktops, as they require less hardware and maintenance. With virtual desktops, businesses can save on the costs of purchasing and maintaining hardware, as all computing resources are provided by the virtual desktop provider.
Additionally, virtual desktops are scalable, so businesses can easily increase or decrease their computing resources as needed. Must Read- Best Virtual AI Girlfriend App
Types of Virtual Desktops
As technology continues to evolve, businesses are constantly looking for ways to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve productivity. One such way is through the use of virtual desktops.
Virtual desktops are a type of technology that allows a user to access a remote desktop environment from any device, including laptops, tablets, and mobile devices.
Now, we will discuss two types of virtual desktops – Hosted Virtual Desktops and Remote Desktop Services – and provide practical examples of their use.
#1 Hosted Virtual Desktop
A hosted virtual desktop, also known as a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), is a type of desktop virtualization that allows a user to access a virtual desktop environment hosted on a remote server.
The virtual desktop is delivered to the user’s device through a remote display protocol, providing an experience similar to a traditional desktop computer.
This type of virtual desktop is ideal for businesses that want to provide their employees with a consistent, secure, and easily managed desktop environment.
Hosted Virtual Desktop Example
A law firm with multiple locations can use a hosted virtual desktop to provide its employees with access to the same desktop environment, applications, and files, regardless of their physical location.
This enables them to work from anywhere, without the need for expensive hardware or IT support.
#2 Remote Desktop Services
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), also known as Terminal Services, is a type of virtual desktop that allows a user to access a desktop environment hosted on a remote server. Unlike a hosted virtual desktop, which provides a virtual machine environment, RDS provides access to a shared desktop environment.
This type of virtual desktop is ideal for businesses that need to provide their employees with access to specific applications or resources.
Remote Desktop Services Example
A call center can use RDS to provide its agents with access to a specific application, such as a customer relationship management (CRM) system, to manage customer interactions.
This enables them to work from anywhere, without the need for expensive hardware or IT support.
Virtual desktops are an excellent way for businesses to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve flexibility. Hosted virtual desktops and Remote Desktop Services are two types of virtual desktops that businesses can choose from, depending on their specific needs.
By choosing the right virtual desktop solution, businesses can provide their employees with a consistent, secure, and easily managed desktop environment that enables them to work from anywhere.
How does a virtual desktop work?
Virtual desktops have become a popular solution for organizations that want to provide their employees with the flexibility to work from anywhere while still ensuring that sensitive data is secure.
here, we will explore how virtual desktops work, including the basics of virtualization, the role of the hypervisor, and the role of the virtual machine.
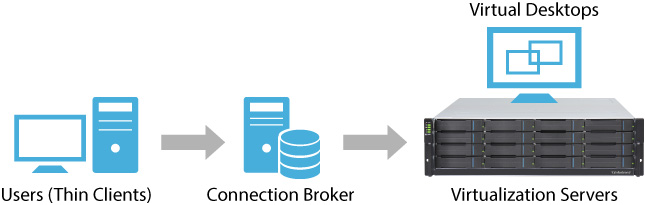
Basics of virtualization: Virtualization technology separates the operating system and applications from the underlying hardware. This allows multiple virtual machines to share the same physical resources, making it possible to deliver desktops to users over a network.
The role of the hypervisor: A hypervisor is a software layer that sits between the physical hardware and the virtual machines. It enables the creation and management of multiple virtual machines on a single physical host. The hypervisor also abstracts the physical resources of the host and presents them to the virtual machines as virtual resources.
The role of the virtual machine: Each virtual machine is a self-contained computing environment that includes an operating system, applications, and data. Users access their virtual desktops using a remote display protocol, which transmits the display of the virtual desktop to the client device and sends input back to the virtual machine.
Virtual desktops offer many benefits, including improved security, easier management, and the ability to access desktops from anywhere, on any device.
They are widely used in businesses, education, and healthcare, as well as for personal use.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Virtual Desktops
Virtual desktops have been growing in popularity due to the benefits they offer. However, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Let’s take a look at both.
Benefits
Drawbacks
Conclusion
In summary, virtual desktops offer a wide range of benefits for businesses and individuals alike, including cost savings, increased mobility and flexibility, enhanced security, and simplified management.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider, such as high bandwidth usage, limited customization options, and dependence on internet connectivity.
Overall, the decision to implement a virtual desktop environment will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific needs and goals of the organization, the available resources, and the technical expertise of the IT team.
It’s important to carefully evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of virtual desktops before making a decision.
Despite the drawbacks, virtual desktops remain a popular and effective solution for many organizations, and they are expected to become even more important as remote work and cloud computing continue to gain popularity.
By understanding the basics of how virtual desktops work and the benefits they offer, businesses can make informed decisions about their IT infrastructure and stay ahead of the curve in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Read More Article :
Hi guys, myself Gabriel Geekstar, as a cloud server engineer with 5 years of experience in web hosting industry, I have developed a deep understanding of the intricacies of web hosting, cloud and virtual server management. My experience in managing web servers has allowed me to develop a keen eye for detail, ensuring that all websites hosted on my servers are running smoothly and efficiently. You can follow me on Twitter, Linktree, Quora and other social media channels.

